WiFi has come a long way since its inception, and with the rise of connected devices, its evolution continues to be a critical component of modern networking. Each new version of WiFi has brought better performance, faster speeds, and improved connectivity. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the differences between WiFi 5, WiFi 6, WiFi 6E, and the emerging WiFi 7, breaking down their unique features and what they mean for users.
What Is WiFi?
Before comparing WiFi versions, it’s important to understand WiFi itself. WiFi, short for “Wireless Fidelity,” is a technology that allows devices to connect to the internet or each other without using physical cables. It operates using radio waves, primarily in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, but as newer versions have emerged, so have additional bands like 6 GHz (for WiFi 6E and WiFi 7).

WiFi 5 (802.11ac): The Fifth Generation of WiFi
WiFi 5, also known as 802.11ac, was introduced in 2014 and primarily operates on the 5 GHz band. It brought substantial improvements over WiFi 4 (802.11n), including faster speeds and better performance in environments with multiple devices.
Key Features of WiFi 5:
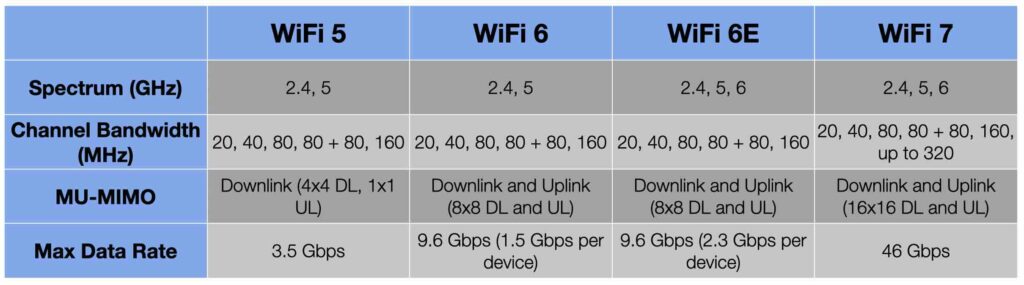
- 5 GHz Band: WiFi 5 exclusively uses the 5 GHz band, which provides faster speeds but with slightly less range compared to 2.4 GHz.
- MU-MIMO Technology: WiFi 5 introduced MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output), allowing multiple devices to receive data simultaneously, reducing wait times.
- 256-QAM Modulation: It uses 256-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), which helps deliver higher data rates.
- Speeds up to 3.5 Gbps: WiFi 5 can theoretically deliver speeds up to 3.5 Gbps, making it a significant improvement over previous versions.
However, despite these benefits, WiFi 5 faced challenges in crowded networks, where many devices competed for bandwidth, reducing overall performance.
WiFi 6 (802.11ax): Faster and More Efficient
WiFi 6, launched in 2019, represents a major upgrade in terms of speed, efficiency, and capacity. It aims to improve performance in dense environments, like homes with multiple smart devices or busy public spaces.
Key Features of WiFi 6:
- Dual-Band Support: WiFi 6 operates on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, enhancing connectivity and ensuring better coverage.
- OFDMA Technology: WiFi 6 introduces Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), allowing it to divide channels into smaller sub-channels. This enables simultaneous data transmission to multiple devices, improving efficiency.
- 1024-QAM Modulation: WiFi 6 uses 1024-QAM modulation, which boosts throughput by increasing the data sent per transmission.
- Target Wake Time (TWT): This feature helps devices reduce power consumption by scheduling transmissions, which is especially beneficial for battery-powered IoT devices.
- Speeds up to 9.6 Gbps: WiFi 6 can theoretically reach speeds of up to 9.6 Gbps, more than double that of WiFi 5.
WiFi 6 is designed to handle crowded networks more effectively, making it ideal for smart homes, businesses, and densely populated urban areas.
WiFi 6E: Extending WiFi 6 into the 6 GHz Band
WiFi 6E takes all the advantages of WiFi 6 and adds access to the newly opened 6 GHz band, which has much wider channels, resulting in less interference and even faster speeds.
Key Features of WiFi 6E:
- 6 GHz Band: WiFi 6E introduces the 6 GHz band, which includes 59 non-overlapping channels, providing much more bandwidth and reducing network congestion.
- Better Capacity: With the additional spectrum, WiFi 6E can support more devices without sacrificing performance, making it perfect for environments like large offices or event spaces.
- Improved Speeds and Latency: The extra bandwidth of the 6 GHz band results in faster speeds and lower latency, ideal for applications like VR/AR, online gaming, and 4K/8K video streaming.
- Speeds up to 9.6 Gbps: Like WiFi 6, WiFi 6E offers speeds up to 9.6 Gbps but can achieve these speeds more reliably due to the less congested 6 GHz band.
While WiFi 6E is a significant upgrade, it requires new hardware, as older WiFi 6 devices can’t utilize the 6 GHz band.
WiFi 7 (802.11be): The Next Generation of WiFi
WiFi 7, also known as 802.11be, is the latest iteration of WiFi, and it’s set to deliver groundbreaking improvements in speed, capacity, and efficiency. While it’s still in the development phase, WiFi 7 routers and devices are expected to be available starting in 2024.
Key Features of WiFi 7:
- Multi-Band Support: WiFi 7 will utilize 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands, ensuring maximum bandwidth and flexibility.
- 320 MHz Channel Width: WiFi 7 will support up to 320 MHz channel width, which is double that of WiFi 6E, allowing it to deliver even higher speeds.
- 16×16 MU-MIMO: WiFi 7 will support 16×16 MU-MIMO, increasing the number of simultaneous data streams and enhancing performance in highly dense environments.
- 4K-QAM Modulation: WiFi 7 introduces 4K-QAM modulation, which can boost throughput by approximately 20% compared to 1024-QAM.
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO): One of the standout features of WiFi 7 is Multi-Link Operation, allowing devices to transmit data across multiple frequency bands simultaneously. This reduces latency and increases reliability.
- Speeds over 40 Gbps: WiFi 7 could theoretically achieve speeds of up to 46 Gbps, making it a game-changer for high-demand applications like 8K video streaming, cloud gaming, and large file transfers.

Choosing the Right WiFi for You
So, how do you decide which WiFi version is right for you? It largely depends on your current setup, the number of devices you have, and your specific network needs.
- If you have a basic home network: WiFi 5 may still be sufficient if you have fewer devices and only use the internet for standard browsing and video streaming.
- If you have a smart home or work from home: WiFi 6 offers better efficiency, especially if you have a lot of connected devices.
- If you need extra bandwidth and less congestion: WiFi 6E is ideal, particularly for environments with many devices or if you frequently use high-bandwidth applications.
- If you want the latest and greatest: WiFi 7 will be the most advanced option, offering unprecedented speeds and multi-link capabilities.
Final Thoughts: WiFi’s Evolution for a Connected Future
The evolution in WiFi reflects a broader trend towards faster, more reliable, and more efficient wireless networking. As more devices become connected—whether at home, at work, or on the go—the demand for better WiFi will continue to grow.
To explore the best routers for your WiFi needs, check out the 5Gstore Router Comparison Tool, where you can compare the features of WiFi 5, WiFi 6, WiFi 6E, and soon, WiFi 7 routers. Additionally, check the ‘5Gstore Summary’ analysis to understand our expert recommendations and find the perfect match for your home or office network.
Stay connected, stay fast!

