This is the second part of the multipart FAQ series on cellular connectivity modules used for IoT applications. We discuss how u-blox, Sierra Wireless, SIMCom, and Ericsson lead the technology with their custom products for 5G, 4G, LTE, LPWA, and 2G applications.
u-blox cellular connectivity modules
u-blox, a Swiss-based technology company specializing in wireless communication, offers various cellular IoT modules such as the SARA, LENA, LARA, and LEXI series. All the series are land grid array (LGA) modules and support power-saving modes like PSM and eRDX with global navigation satellite system (GNSS) support, either integrated or via external control. Except for LEXI, all the series are built to accommodate the nested design of u-blox technologies, as shown in Figure 1. However, each of the series is also unique in its way.
Figure 1. u-blox’s nested design allows integration of the SARA, LARA, and LENA module series and enables smooth migration between cellular technologies. (Image: u-blox)
The SARA series is meant for LTE Cat 1bis, LTE-M, NB-IoT, SAT, and 2G technologies with a form factor of 16.0 x 26.0 x 2.2-3.0 mm. The LARA series covers the LTE Cat 1 and Cat 4 technologies at 24.0 x 26.0 x 2.6 mm form factor. The LENA series specializes in LTE Cat 1bis technology with a slightly bigger form factor of 27 x 30 x 2.6 mm. The LEXI series offers the least form factor at 16.0 x 16.0 x 2.0 mm, covering a wide variety of technologies, i.e., LTE Cat 1bis, LTE-M, NB-IoT, and 2G. A detailed comparison of the different modules and the supported technologies is shown in Figure 2.
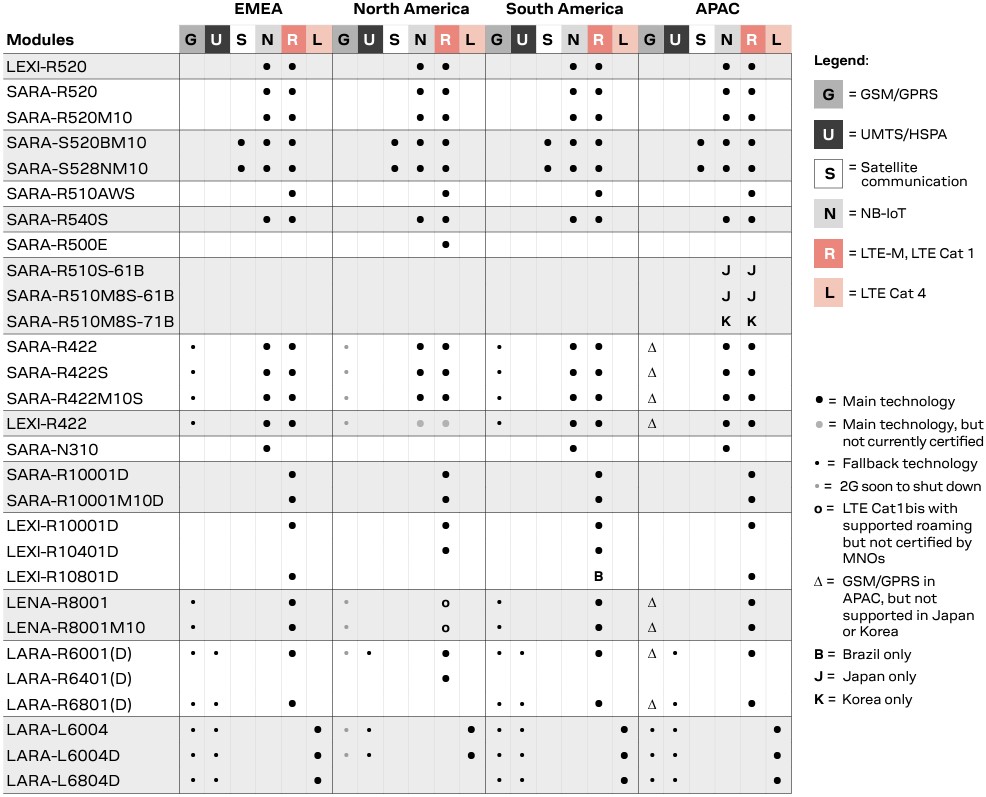
Figure 2. A comparison of the different u-blox cellular connectivity modules. (Image: u-blox)
Sierra Wireless (now Semtech) IoT Modules
Sierra Wireless’s EM Series is a line of cellular connectivity modules designed in the M.2 form factor. This form factor specifies internally mounted computer expansion cards, particularly solid-state drives (SSDs). Figure 3 illustrates the EM series module’s appearance from three different angles.

Figure 3. An all-in-one view illustration of Sierra Wireless’ EM Series 5G modules. (Image: GetWireless)
The EM7565 LTE-Advanced Pro module is an LTE category 12 device with a peak download speed of 600 Mbps and a peak download speed of 150 Mbps. It supports 4G LTE and 3G HSPA+ bands and integrates a GNSS receiver. The EM9291 5G NR Sub-6 GHz module, which also supports 4G LTE (Cat-20) and 3G fallback, can help achieve a higher peak download speed of 4.9 Gbps.
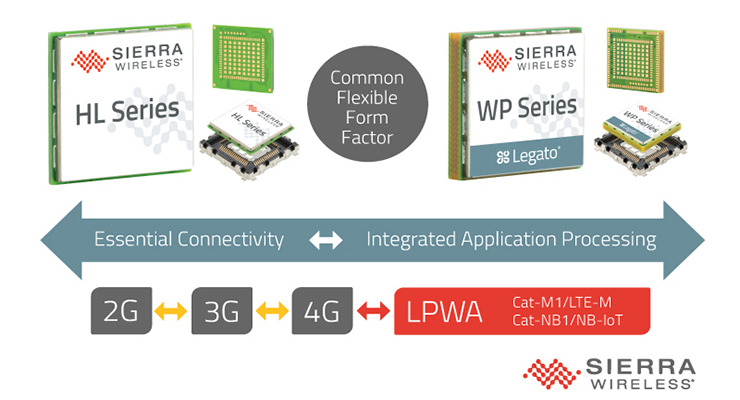
Sierra Wireless also has a range of Low-Power Wide-Area (LPWA) modules with the HL and WP series, as shown in Figure 4. The HL7812 supports multiple LTE bands and a 2G fallback with 3GPP release 14 compliance. It has a high transmit power of at least 23 dBm, ensuring coverage in challenging locations like indoors or deep underground. For applications such as consumer wearables, health monitoring devices, and tracking devices, the WP7702 module is suitable. Its 2G fallback feature ensures continued connectivity at slower speeds due to tracking in areas with lower network connectivity.
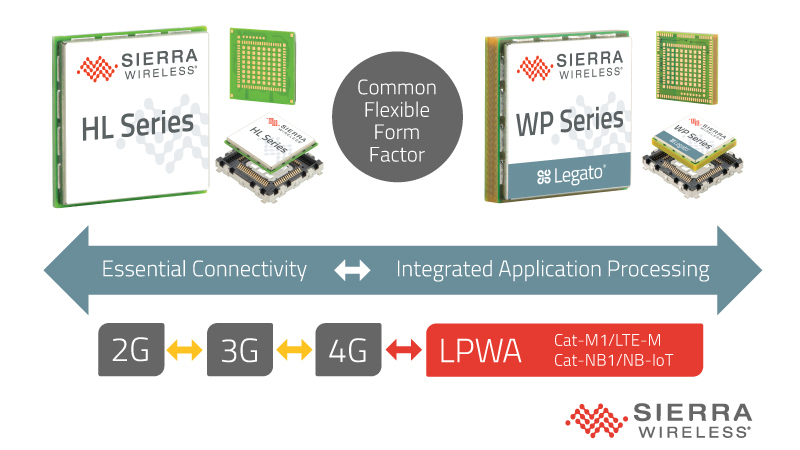
Figure 4. Sierra Wireless LPWA modules consist of LTE networks’ HL and WP series. (Image: Business Wire)
SIMCom wireless solutions
With the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) worldwide, a dedicated cellular connectivity module for AI, like the SIM9650L from SIMCom, is a promising candidate. It runs on Android 14 OS and is equipped with an Octa-core 64-bit ARM V8 processor and Andreno 643 GPU. It integrates AI processors Dual HVX and Hexagon Tensor Accelerator, delivering computational power of over 14 tera operations per second (TOPS) for AI applications.
The SIM7070G is an LPWA module. Its PSM and eDRX modes can extend the battery life to 10 years for IoT applications, as it consumes only 14 mA under low-power mode. The module is 24 x 24 mm compact and adopts a leadless chip carrier (LCC) form factor, which is good for product designs. Figure 5 shows how the SIM7070G module can be mounted on the Raspberry Pi 4 module for quick IoT applications.

Figure 5. The SIM7070G LPWA module mounted on the popular Raspberry Pi 4. (Image: ABRA Electronics Corp)
Ericsson’s dual-mode 5G core
Ericsson’s dual-mode architecture for 5 G technology offers a unique approach to cellular connectivity for IoT applications. The dual-mode 5G Core (5GC) combines evolved packet core (EPC) and 5GC network functions into a common cloud-native platform. This allows for an efficient total cost of ownership and smooth migration from 4G to 5G. Figure 6 shows the integrated EPC and 5GC network functionality into the dual-mode architecture.
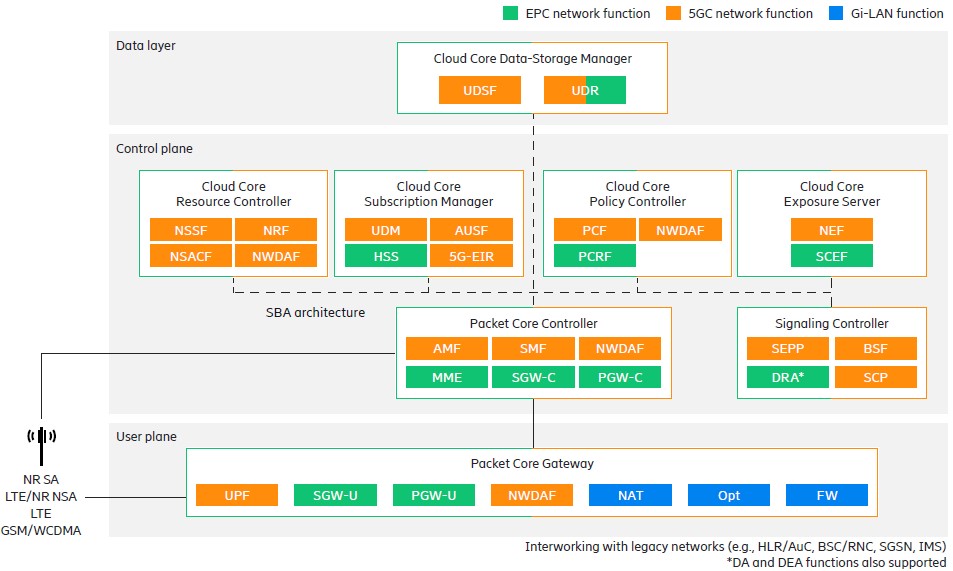
Figure 6. Ericsson’s dual-mode 5G Core portfolio combines EPC and 5GC network. (Image: Ericsson)
The solution is built on cloud-native principles and microservices, offering high deployment flexibility and operational efficiency in a multi-access cloud-native platform. It supports centralized and distributed deployments, allowing service providers to tailor their networks based on specific use cases and traffic patterns.
The built-in network slicing capabilities allow service providers to segment the network and deploy multiple logical networks for different service types over a common infrastructure. This enables them to cater to diverse customer needs and business models efficiently.
Summary
The four manufacturers’ cellular connectivity modules discussed in this FAQ share many features, such as M2M applications, GNSS support, a compact form factor, and a few unique features for each module. u-blox’s nested design allows for integrating multiple modules on its development boards, making it easy to migrate between cellular technologies. Sierra Wireless’ M.2 form factor is helpful for SSDs with LPWA options.
SIMCom modules have additional form factors to support LCC+LGA and 77PIN for remote tracking. Ericsson’s modules are dedicated to 5G advancements in dual-mode 5GC, which opens up innovations that combine EPC and 5GC. The choice of modules depends on the engineer’s need and customer applications.
References
u-blox raises the bar with 5G-ready cellular module and chipset for low power wide area IoT applications, Kudelski IoT
SIMCom unveils optimised LTE CAT 1 bis module SIM7672x series to address cellular IoT market, IoT Now
SIM7070G Global NB-IoT Communication Module with GNSS Positioning, DFRobot
SIM7080G module LPWA wireless solutions, SIMCom Wireless Solutions Limited
WP7702 LPWA module | LTE-M and NB-IoT with 2G fallback, Sierra Wireless
SIM7070G Module LPWA Wireless Solutions, SIMCom Wireless Solutions
HL7812 LTE-M and NB-IoT Module for Industrial IoT, Sierra Wireless
IoT modules – secure cellular solution, Sierra Wireless
EM7565 LTE-Advanced Pro Module, Sierra Wireless
EM9291 5G NR Sub-6 GHz Module, Sierra Wireless
Download your guide: From EPC to 5GC, Ericsson
One Core- the best of the two worlds, Ericsson
Dual-Mode 5G Cores: TCO benefits, Ericsson
What is the M.2 form factor?, everything RF
u-blox cellular product overview, u-blox
Cellular chips and modules, u-blox
Cellular product line card, u-blox
Related EE World content
When cellular connections are the only option – 5G Technology World
What are 5G’s, the different types, and how are they used?
IoT via Cellular: Out with 2G and 3G, in with LPWA
What to expect from 5G-Advanced?
IoT: How 5G differs from LTE?
IoT connectivity: 4G or 5G?