Maintaining a stable and efficient WiFi network can sometimes feel like a challenge, especially with the increase in devices connected to the Internet today. By following best practices like leveraging multiple frequency bands, optimizing WiFi channels, setting up Quality of Service (QoS) rules, and keeping your firmware up to date, you can ensure a more reliable and faster WiFi experience. Here’s how each of these methods helps improve WiFi performance—and a few more expert tips to optimize your network.
1. Use Multiple WiFi Frequency Bands
Modern WiFi routers and access points often operate on multiple frequency bands, mainly 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, and newer models also offer 6 GHz with WiFi 6E. Each frequency has its strengths:
- 2.4 GHz: Better range but slower speeds. Ideal for devices further away from the router or those that don’t need high bandwidth, like smart home devices.
- 5 GHz: Faster speeds but a shorter range. Perfect for devices closer to the router or where you need high-speed access, like streaming or gaming.
- 6 GHz: Offers faster, interference-free connectivity for WiFi 6E-compatible devices, especially in densely populated areas.
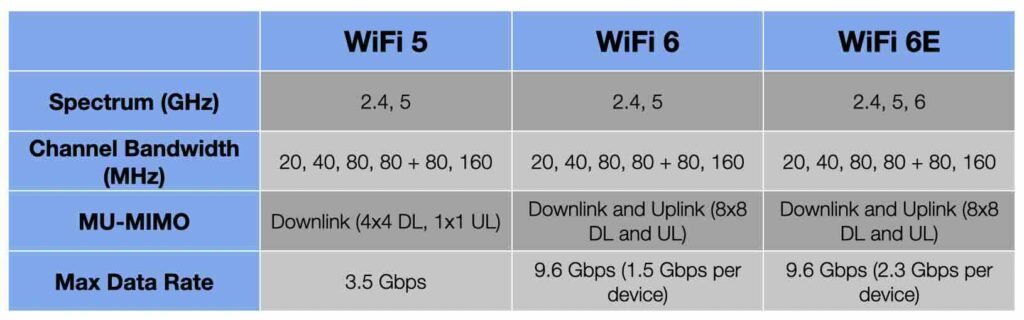
To better understand how frequency bands can help improve WiFi performance, here’s a breakdown of some key differences. This includes
spectrum, channel bandwidth, MU-MIMO support, and maximum data rates for WiFi 5, WiFi 6, and WiFi 6E. These distinctions highlight how each generation of WiFi builds on the previous one to offer improved performance, connectivity, and efficiency:
- Spectrum:
- WiFi 5 operates primarily on the 5 GHz band, though also supports 2.4 GHz. 5 GHz is preferred as it provides higher data rates but shorter range due to less wall penetration.
- WiFi 6 supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, offering greater flexibility and backward compatibility with older devices while improving speed and efficiency.
- WiFi 6E adds a new 6 GHz band in addition to the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, significantly expanding the available spectrum and reducing interference from neighboring networks. This enables faster connections and a more stable network, especially in crowded environments.
- Channel Bandwidth:
- WiFi 5 typically supports up to 80 MHz channels, though some higher-end implementations can handle 160 MHz.
- WiFi 6 improves bandwidth support to 160 MHz, which enhances speed and data-carrying capacity for devices that can utilize it.
- WiFi 6E also supports 160 MHz channels but with the advantage of the 6 GHz spectrum, which allows for a higher number of these wider channels, making it ideal for high-density scenarios with many connected devices.
- MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output) Support:
- WiFi 5 introduced downlink MU-MIMO, allowing multiple devices to receive data simultaneously, which was beneficial for download-heavy environments but didn’t support upload improvements.
- WiFi 6 enhanced this by adding uplink and downlink MU-MIMO with up to eight streams, allowing for faster communication between multiple devices and the router in both directions.
- WiFi 6E continues to support uplink and downlink MU-MIMO, taking advantage of the less congested 6 GHz band, leading to less interference and better performance in busy environments.
- Maximum Data Rate:
- WiFi 5 achieves a maximum data rate of around 3.5 Gbps under ideal conditions using 160 MHz channels.
- WiFi 6 increases the maximum data rate to 9.6 Gbps, thanks to improved modulation (1024-QAM), efficient spectrum use, and broader channel bandwidth.
- WiFi 6E also reaches a theoretical maximum of 9.6 Gbps, but the 6 GHz spectrum provides a more consistent and high-speed connection with reduced latency and less interference, ideal for applications like VR, gaming, and 8K streaming.
With these advancements, WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E offer a notable step up in performance, especially for environments with many connected devices. Here’s a summary table to add further clarity:
By connecting devices to the appropriate band, you can improve WiFi performance across your home, reducing congestion and enhancing speed.
2. Manually Set WiFi Channels
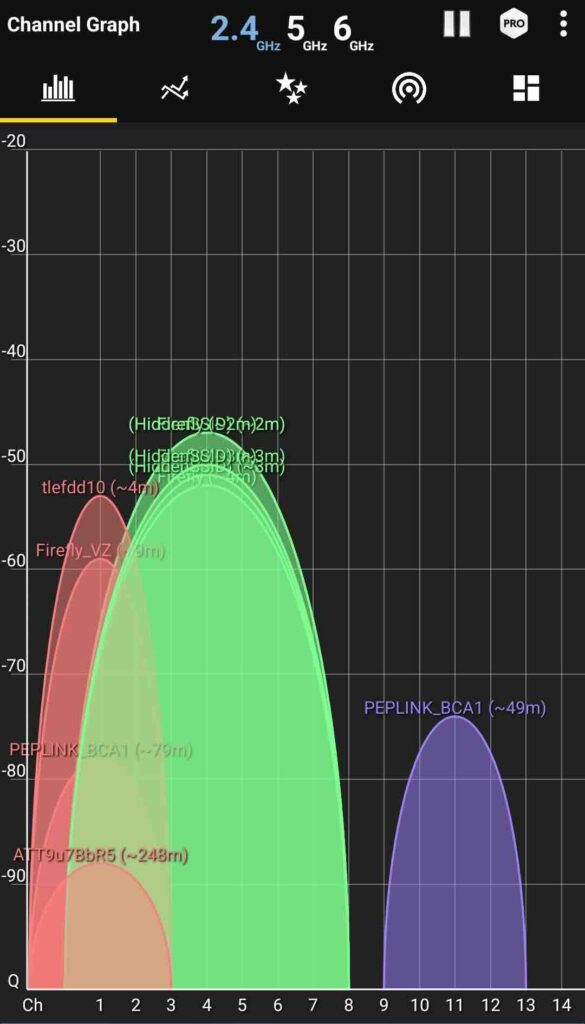
Routers often select channels automatically, but in crowded areas, interference from neighboring networks can slow things down. To optimize:
- Check for Interference: Use a WiFi analyzer app to identify the least congested channel in your area.
- Select Optimal Channels: For the 2.4 GHz band, choose channels 1, 6, or 11, which don’t overlap. On 5 GHz, more channels are available, so select one with minimal interference.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting your WiFi channels can help improve performance and reduce dropped connections.
3. Implement Quality of Service (QoS) Rules
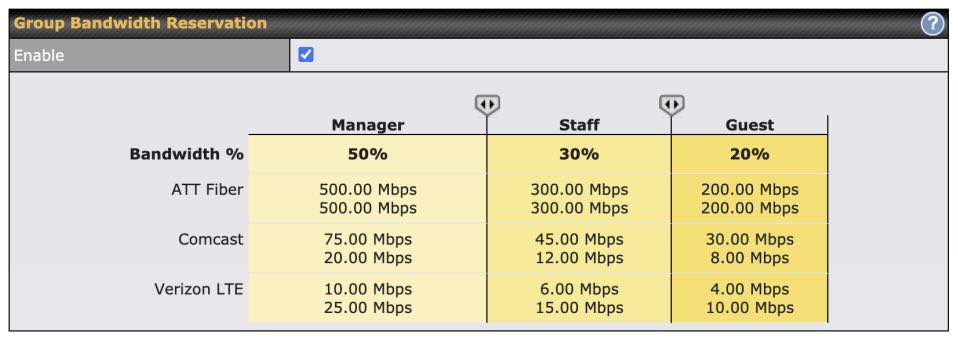
Quality of Service (QoS) rules allow you to prioritize certain types of traffic on your network, ensuring that high-demand activities like streaming or video conferencing get the necessary bandwidth. To set up QoS:
- Identify Priority Devices: In your router’s QoS settings, identify devices or activities that require the most bandwidth (like a laptop for work calls).
- Allocate Bandwidth: Many routers allow you to assign a percentage of bandwidth to high-priority devices or activities, helping avoid buffering during critical tasks.
QoS is especially helpful in households with many devices, preventing low-priority traffic from slowing down essential applications.
Here are some examples of what QoS settings may look like on your router:
4. Perform Regular Firmware Updates
Firmware updates often bring security patches, bug fixes, and performance enhancements that help your router run smoothly and securely. To ensure updates don’t go unnoticed:
- Set Up Notifications: Some routers offer notifications for updates.
- Automate Where Possible: Many modern routers offer a simple click to update firmware. This helps keep your device up-to-date without much effort on your part.
A router with updated firmware is less likely to experience security issues or performance lags, helping improve WiFi performance and stability.
5. Position Your Router Properly
Proper router placement is critical for maximizing WiFi coverage and minimizing interference. A few key points to consider:
- Find a Central Location: Place the router near the center of your home, ideally on the main floor, to allow for more even distribution of the WiFi signal. Placing it in a corner or in a far room can limit its range, resulting in weak spots on the other side of the home.
- Avoid Physical Obstructions: Walls, floors, large furniture, and appliances can interfere with WiFi signals. Position the router away from thick walls, metal objects, and mirrors, which can reflect and distort signals. The fewer obstructions, the better.
- Elevate the Router: Placing the router on a shelf or mount rather than on the floor can improve coverage, especially if you have multiple floors. WiFi signals tend to travel outward and downward, so an elevated router can help reach devices on both the main and upper floors.
- Reduce Interference from Other Electronics: Devices like microwaves, cordless phones, and baby monitors operate on similar frequencies and can interfere with WiFi. Keep the router away from such devices to avoid connection disruptions.
By positioning your router carefully, you can maximize its range, reduce interference, and create a stronger connection across all rooms.
Additional Tips to Improve WiFi Performance
a. Minimize Interference from Other Devices
Devices like cordless phones, baby monitors, and microwaves can disrupt WiFi signals. Ensure your router is positioned at a distance from such devices to avoid signal interference.
b. Regularly Reboot Your Router
A quick reboot clears out the router’s cache and can improve performance. Consider scheduling a reboot weekly or bi-weekly, especially if you notice slower speeds.
c. Use a WiFi Extender or Mesh Network
If you have a large home or multiple floors, a single router may not be enough. WiFi extenders or mesh networks can improve coverage, but also improve WiFi performance. While providing more range for your devices, they also help to better maintain the stability of your connection.
d. Secure Your Network
Limiting access to your network can reduce load and increase speed for trusted devices. Use WPA3 or WPA2 encryption, avoid sharing your network password, and consider setting up a guest network for visitors.
Key Takeaways on How to Improve WiFi Performance
- Use Multiple Frequency Bands: Assign devices to appropriate bands based on their distance and bandwidth needs.
- Optimize WiFi Channels: Select less crowded channels to minimize interference.
- Set Up QoS Rules: Prioritize bandwidth for essential applications and devices.
- Keep Firmware Updated: Regular updates improve performance and security.
- Additional Steps: Position your router well, reduce interference, reboot periodically, and consider network extenders or mesh setups for large spaces.
FAQs
Q1: How often should I update my router’s firmware?
Most routers don’t need frequent updates, but checking every few months is wise. Many new routers offer automatic updates, ensuring your device remains secure and efficient.
Q2: What’s the difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands?
The 2.4 GHz band offers longer range but slower speeds, while the 5 GHz band provides faster speeds at a shorter range. The newer 6 GHz band is faster still but requires WiFi 6E-capable devices.
Q3: Do I need a mesh network to improve WiFi performance?
If your home is large or has many obstacles, a mesh network or extender can improve coverage. For smaller spaces, optimizing the main router’s position and settings may be sufficient.
Q4: How can QoS rules benefit my home network?
QoS rules prioritize certain types of traffic, ensuring important activities like streaming or video calls receive adequate bandwidth, even with multiple devices online.
Q5: Is rebooting the router regularly necessary?
Yes, a quick reboot every week or two clears out temporary data and can help maintain speed and stability.
By implementing these tips and best practices, you can enjoy a more robust and stable WiFi network, supporting smooth connectivity for all your devices and activities.

